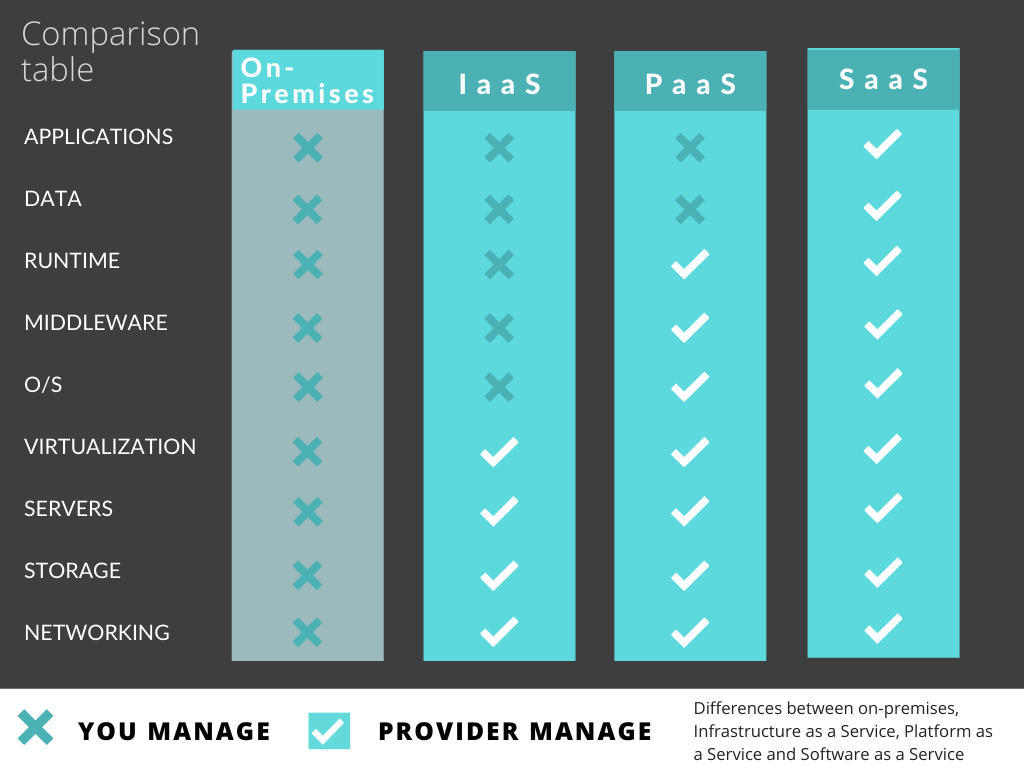
Cloud computing consists of three main categories which are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS and they stand for Infrastructure as a service, Platform as a service, and Software as a service respectively. IaaS is the most basic among them. The keyword infrastructure ‘I’ relates to computing, storage, and networking while the keyword ‘aaS’ defines a shared, hourly, or monthly billing, contractless, and self-service type of service. The infrastructure in the cloud which is so-called as data centers, by the providers/vendors. The customers of IaaS can rent a space to the virtual data center and access these infrastructures on the cloud over the internet. In this article, you are going to learn about the cloud infrastructure, advantages, disadvantages of IaaS, and some additional information about it. So, keep on reading!
Cloud Infrastructure of IaaS
The cloud infrastructure of IaaS can be categorized into three groups which are:
1. Compute
For computing, IaaS is the virtual machine in the cloud whereby it is not on a fixed piece of hardware but it is anywhere on the provider’s servers. IaaS commonly includes GPUs and CPU and they are used for different types of workloads. The providers are managing the hypervisors so that the customers can get their desired amount of computing based on the pay-for-what-you-use basis.
2. Storage
The target items for cloud storage include objects, files, and blocks. Object storage is the most common among them because it provides more benefits which are security, flexibility, and scalability for large volumes of unstructured data. These unstructured data include music, image, and video files. We can simply access them through APIs or Http/Https. For block storage, the storage volume is treated as an independent disk drive and has a fixed-sized capacity. The cloud infrastructure of IaaS allows the user to store, back up, restore and recover data whenever in need.
3. Networking
Through API, the traditional networking hardware such as routers and switches now become available programmatically. We also call the networking in the cloud as a form of Software Defined Networking. Furthermore, there are more advanced networking such as virtual private cloud and multi-zone regions construction and they will soon be discussed further in upcoming articles.
Besides that, IaaS allows the testing and development of applications and website hosting. It also supports traditional enterprise applications, for example, ERP and other business analytic applications.
Advantages (Pros) of IaaS
Reduce expenditures
As compared to on-premises, IaaS helps to reduce the cost of expenditures of the businesses. The organization which uses IaaS will no longer have to pay extra costs on buying, managing, and maintaining their infrastructure. IaaS only requires you to pay for what you use and the other extra resources can be excluded if they are not necessarily needed.
Security
IaaS provides a high level of security. This has been proved as the infrastructure is always being stored in safe data centers by the providers. Customers can always recover the data easily. A bonus point, the providers also use firewalls, encryption, and professional tools to avoid cybercrime and fraud.
Reduce downtime
IaaS provides more disaster recovery options, which reduces the downtime as compared to on-premise deployments. It allows instant recovery for any outages that occur.
Pay-as-you-go
Unlike the on-premise infrastructure, IaaS does not cost you upfront and capital expenditures. The provider will bill based on the usage-based metrics.
Increase Overall Speed
The speed of executions on the overall infrastructure is increased when using IaaS. For example, the on-premise infrastructure consumes weeks or months to provision applications. IaaS only requires a few minutes to provision the entire application environment.
Disadvantages (Cons) of IaaS
Lack of Support
It is often difficult to get live help and support on the spot when in need. Even if it is available, the guidance might not fully solve the problem due to the absence of mature service providers.
Unexpected Costs
When it comes to months with peak usage, the monthly cost may increase.
Security Risks
Since the providers only take charge of the infrastructure security, the businesses will have to be responsible for anything they host on their own.
Additional Information